Module 1: CSM Foundations: Strategy, Responsibilities, and Value
Listen Audio 🎧
Audio Version - Listen to this module on-the-go. Perfect for commutes or multitasking. Duration: 14:05 minutes
What You'll Learn (Audio Version)
- Understand that CSMs are proactive guides who ensure customers achieve desired outcomes, differentiating from reactive Support that resolves issues and transactional Sales that closes deals—CSMs build long-term strategic partnerships focused on customer lifetime value
- Master the three core CSM characteristics: proactively identifying risks and opportunities through health score monitoring 60-90 days before renewal, building strong trust-based relationships by understanding customer business objectives beyond product usage, and balancing customer advocacy with organizational goals through win-win solutions
- Apply the CSM Funnel Framework across three concurrent stages: Adoption focuses on onboarding and early usage in days 0-90, Expansion identifies upsell opportunities in months 3-12 through business reviews and usage analysis, and Renewal secures contracts 90-120 days before expiration through risk mitigation and ROI demonstrations
- Position yourself as an organizational bridge by feeding customer intelligence to Product, Marketing, and Sales teams while advocating internally for customer needs—create weekly Customer Intel briefs summarizing 3-5 key insights to build cross-functional influence and demonstrate strategic value
- Establish yourself as a trusted advisor through the three-attribute framework: Credibility by mastering product capabilities and industry knowledge, Reliability by delivering on every commitment without exception and maintaining proactive communication, and Empathy by listening to understand before proposing solutions and celebrating customer wins as your own
Watch Video 📹
Video Version - Watch the complete video tutorial with visual examples and demonstrations. Duration: 6:24 minutes
Read Article 📖
Learning Objectives:
- Define the CSM role and its importance in SaaS businesses
- Understand core responsibilities like onboarding, adoption, and advocacy
- Explore collaboration strategies across teams like Sales, Product, and Support
- Differentiate CSM role from Sales and Support functions
- Apply the Trusted Advisor Framework to build customer credibility
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Introduction
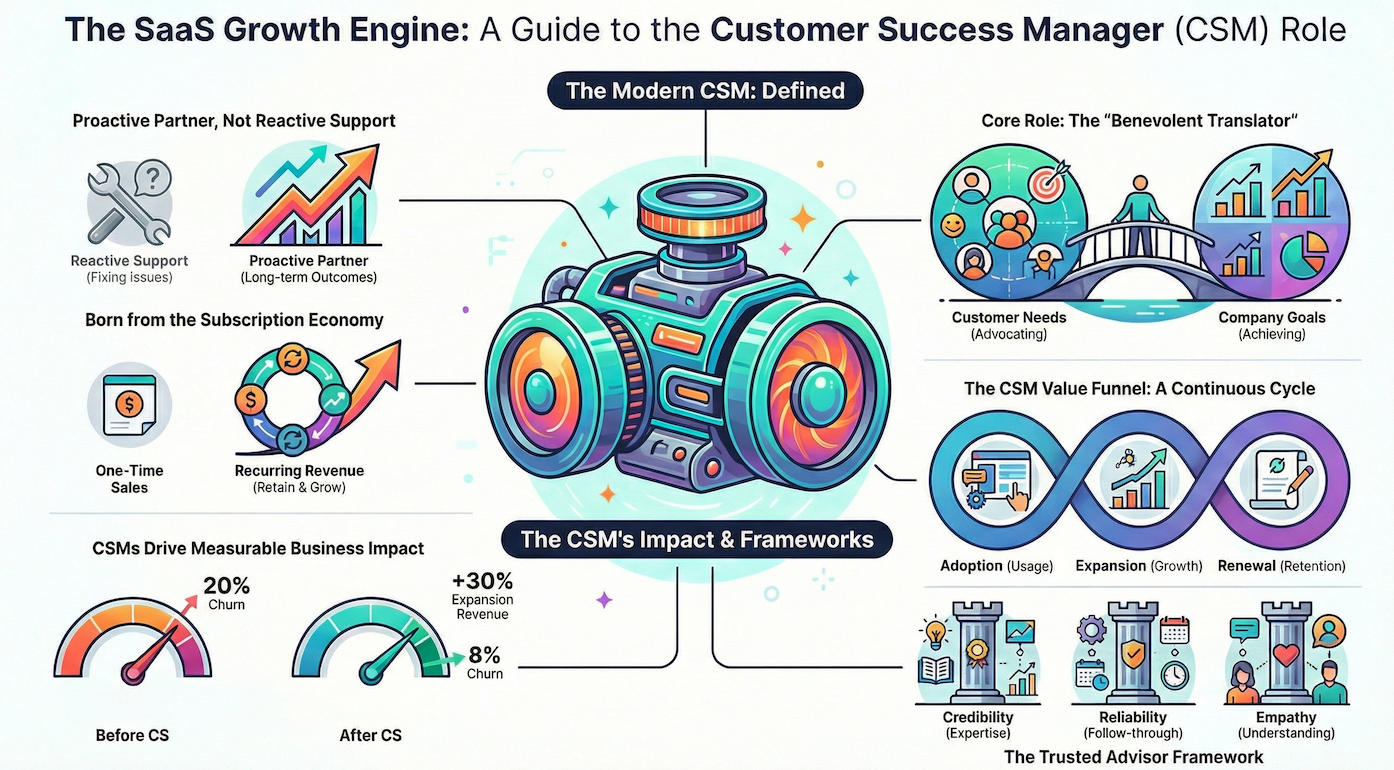
The Customer Success Manager is the proactive guide and advocate for the customer in a SaaS organization. While roles like Sales focus on acquisition and Support on issue resolution, the CSM ensures customers achieve their desired outcomes using the product. They are both a strategic partner to customers and a growth enabler for the company.
The Cost of Not Having Strong CSMs
Without effective Customer Success Management, SaaS companies face:
- Increased churn - Customers fail to see value after onboarding and abandon the product within 6-12 months
- Poor product alignment - Without proactive engagement, customer feedback doesn't inform product decisions or roadmap priorities
- Stagnant revenue - Missed opportunities for upsells and expansions mean flat or declining ARR growth
- Weak customer relationships - Reactive-only engagement creates transactional relationships instead of strategic partnerships
- Lost market intelligence - Missing critical insights from customers that could drive competitive advantage
The Benefits of Strategic Customer Success
Strong CSM function delivers measurable business impact:
- Revenue predictability - Retention drives consistent, recurring revenue streams that are more valuable than new sales
- Cost efficiency - Retaining an existing customer is 5-7 times cheaper than acquiring a new one
- Long-term loyalty - Satisfied customers become advocates, providing testimonials, referrals, and word-of-mouth marketing
- Product intelligence - Direct customer feedback loop accelerates product-market fit and feature prioritization
- Expansion opportunities - Deep customer relationships reveal upsell and cross-sell opportunities organically
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
PART 1: DEFINING THE CSM ROLE IN SAAS
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Key Characteristics of a CSM
The most effective Customer Success Managers share three core characteristics that differentiate them from other customer-facing roles:
1. Proactively Identifies Risks and Opportunities
Unlike Support (reactive) or Sales (transactional), CSMs monitor customer health continuously and intervene before problems escalate:
- Track usage patterns and engagement metrics to spot early warning signals
- Identify at-risk accounts 60-90 days before renewal using health scores
- Surface expansion opportunities by analyzing feature adoption and business growth
- Anticipate customer needs based on lifecycle stage and industry trends
Example: A CSM notices a customer's login frequency dropped 40% over two weeks. Instead of waiting for a support ticket or churn notice, they proactively schedule a check-in call, discovering the customer's champion left the company. The CSM facilitates new stakeholder onboarding, preventing churn.
2. Builds Strong, Trust-Based Relationships
CSMs invest in long-term relationships rather than transactional interactions:
- Understand customer business objectives beyond just product usage
- Become familiar with customer team structure, decision-makers, and internal politics
- Demonstrate genuine care for customer success, not just contract renewal
- Maintain consistent communication rhythm tailored to customer preferences
Example: A CSM learns their customer is preparing for an IPO. They proactively provide case studies on how similar companies used the product during high-growth phases, positioning themselves as a strategic partner rather than just a vendor.
3. Balances Customer Advocacy with Organizational Goals
The best CSMs navigate the tension between customer needs and company objectives:
- Advocate for customers internally (product requests, pricing exceptions) while maintaining business viability
- Identify win-win solutions where customer success drives company revenue
- Set realistic expectations with customers about what's possible within company constraints
- Communicate trade-offs transparently when customer requests conflict with business priorities
Example: A customer requests a custom integration that would require significant engineering resources. The CSM advocates internally, gets it prioritized on the roadmap, but also sets realistic timeline expectations with the customer (6 months vs. their hoped-for 1 month).
💡 Pro Tip: The best CSMs are "benevolent translators" - they translate customer needs into business requirements for internal teams, and translate company limitations into customer-friendly explanations. Mastering both languages is key to effectiveness.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Why the CSM Role Exists
The CSM role emerged with the rise of the subscription-based SaaS model, where success depends on retaining and growing customer accounts rather than one-time sales.
The Subscription Economy Shift
Traditional software (pre-2000s):
- One-time license purchase ($50k-500k upfront)
- Implementation projects (6-12 months)
- Maintenance contracts (20% annual)
- Success = "Did it install correctly?"
Modern SaaS model:
- Monthly/annual subscriptions ($500-5k/month)
- Quick onboarding (days to weeks)
- Continuous value delivery required
- Success = "Are they achieving business outcomes?"
This shift created the need for CSMs because:
- Customers can churn monthly if not seeing value
- Revenue is recognized over time, not upfront
- Customer lifetime value (LTV) determines profitability
- Retention and expansion became primary growth drivers
Business Impact: Why Companies Invest in CS Teams
Real-World Example:
A mid-sized SaaS company that focused solely on Sales and Support struggled with a 20% annual churn rate. After introducing a dedicated CSM team to proactively manage customer engagement:
- Churn dropped to 8% within 12 months
- Net Revenue Retention increased from 85% to 112%
- Customer satisfaction (NPS) improved from 32 to 58
- Expansion revenue grew by 30%
- Customer acquisition costs were offset by longer customer lifetimes
The financial math:
- Before CSMs: 100 customers × $10k ARR × 80% retention = $800k retained revenue
- After CSMs: 100 customers × $10k ARR × 92% retention × 12% expansion = $1,030k retained + expansion revenue
- Net impact: $230k additional revenue with 5-person CS team costing $150k = $80k net gain + strategic benefits
💡 Pro Tip: When explaining your role's value to executives or during interviews, lead with retention math. A 5-point improvement in retention (from 85% to 90%) on a $10M ARR base saves $500k annually - far exceeding the cost of a CS team.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
The CSM Funnel Framework
Visualize CSM responsibilities through three stages that map to the customer lifecycle:
Stage 1: Adoption
Focus: Ensure smooth onboarding and drive early product usage
Timeline: Days 0-90
Key Activities:
- Kickoff calls and goal alignment
- Implementation and configuration support
- Initial training and feature walkthroughs
- Early win identification and celebration
- Usage monitoring and proactive outreach
Success Metrics:
- Time-to-first-value (TTFV)
- Feature adoption rate
- User activation percentage
- Onboarding completion rate
Stage 2: Expansion
Focus: Identify opportunities to add value through upsells and cross-sells
Timeline: Months 3-12+
Key Activities:
- Business reviews and ROI demonstrations
- Usage analysis to identify growth opportunities
- Stakeholder expansion to new departments
- Feature education for underutilized capabilities
- Strategic planning sessions
Success Metrics:
- Net Revenue Retention (NRR)
- Expansion revenue generated
- Additional seats/modules sold
- Department penetration
Stage 3: Renewal
Focus: Mitigate churn risks and secure contract renewals
Timeline: 90-120 days before contract end
Key Activities:
- Health score monitoring
- Risk mitigation for at-risk accounts
- Value summary and ROI calculations
- Renewal conversations and negotiations
- Success story documentation
Success Metrics:
- Gross Revenue Retention (GRR)
- Renewal rate
- Churn rate
- Contract expansion at renewal
💡 Pro Tip: Don't think of these as sequential stages - they're concurrent. Even during onboarding (Adoption), you should be identifying expansion opportunities and documenting wins for future renewal conversations. The best CSMs work all three stages simultaneously.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Best Practices for Understanding Your CSM Role
- Study the subscription economics → Understand why retention matters more than acquisition in SaaS business models
- Map your role to business outcomes → Connect your daily activities to metrics like NRR, GRR, and expansion revenue
- Differentiate from Sales and Support → Know when to be consultative (like Sales) vs. reactive (like Support) based on situation
- Work all three funnel stages concurrently → Don't wait for renewal to think about retention; start on day one
- Quantify your impact → Track how your interventions affect churn prevention, expansion, and customer satisfaction
- Build proactive habits → Schedule regular account reviews, monitor health scores weekly, and intervene before customers ask
- Position as strategic partner → Frame conversations around customer business outcomes, not just product features
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
PART 2: CSM AS THE ORGANIZATIONAL BRIDGE
The CSM acts as a critical bridge between customers and internal teams, ensuring alignment and information flow.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Dual Role: Customer Advocate & Company Growth Driver
Customer Advocate Responsibilities
CSMs ensure customer needs are represented internally:
- Voice of Customer (VoC) programs - Systematically collect and share customer feedback with Product, Marketing, and Sales
- Internal escalation management - Champion customer concerns to appropriate teams with urgency and context
- Feature request prioritization - Aggregate customer needs to influence product roadmap decisions
- Customer-centric policy advocacy - Push for policies and processes that improve customer experience
Example: A CSM noticed 15 customers struggling with the same workflow limitation. They consolidated feedback, quantified business impact ($500k ARR at risk), and presented to Product leadership. The feature was prioritized, preventing churn and improving NPS by 12 points.
Company Growth Driver Responsibilities
CSMs align customer goals with organizational objectives:
- Revenue expansion identification - Spot upsell and cross-sell opportunities aligned with customer growth
- Reference customer development - Cultivate satisfied customers into case studies, testimonials, and speakers
- Product adoption acceleration - Drive usage of features that increase stickiness and reduce churn risk
- Competitive intelligence gathering - Understand why customers chose you and what alternatives they consider
Example: During a quarterly business review, a CSM learned the customer was manually exporting data for reports. By demonstrating the automated reporting feature, they created an upsell opportunity ($15k additional ARR) while solving a customer pain point.
💡 Pro Tip: The tension between advocacy and growth is healthy. When you find yourself only advocating (giving discounts, making exceptions) without driving expansion, you're too customer-focused. When you're only pushing upsells without solving problems, you're too company-focused. Balance comes from finding win-win opportunities.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
CSMs as Feedback Hubs
CSMs gather and distribute customer insights to optimize organizational strategy:
What CSMs Feed to Product Teams
- Feature requests with business impact quantification
- Usability issues preventing adoption
- Workflow gaps customers are solving with workarounds
- Competitive feature comparisons from customer evaluations
- Product bugs affecting multiple customers
What CSMs Feed to Marketing Teams
- Customer success stories and use case examples
- Language that resonates with target audience
- Pain points to address in messaging
- Objections heard during renewal conversations
- Ideal customer profile insights
What CSMs Feed to Sales Teams
- Expansion opportunities and warm leads
- Competitor intelligence from customer conversations
- Pricing objections and market positioning insights
- Ideal implementation patterns that predict success
- Reference customer availability and talking points
Example: A CSM at a FinTech company identified customer confusion around a new feature during onboarding calls. Their consolidated feedback led to simplified UI and updated marketing messaging, improving adoption rates by 25% and reducing support tickets by 30%.
💡 Pro Tip: Create a weekly "Customer Intel" brief summarizing 3-5 key insights from customer conversations. Share it with Product, Marketing, and Sales. This 15-minute habit positions you as a strategic contributor and builds cross-functional influence.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Comparison: Sales vs. Support vs. CSM Roles
Understanding how CSM differs from adjacent roles clarifies your unique value:
| Dimension | Sales | Support | CSM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Closing new deals | Resolving issues | Driving customer success |
| Key Metrics | New Revenue (ARR) | Ticket Closure Rates | Retention (NRR, GRR) |
| Engagement Style | Transactional | Reactive | Proactive, Relational |
| Customer Stage | Pre-sale | Any stage (issue-based) | Post-sale, lifecycle-based |
| Time Horizon | Short-term (close deal) | Immediate (fix issue) | Long-term (lifetime value) |
| Success Definition | Deal signed | Ticket resolved | Outcomes achieved |
| Compensation Model | High variable (commissions) | Salary-based | Moderate variable (retention/expansion) |
Why This Unique Position Matters:
By bridging the gap between customer success and company goals, CSMs play a pivotal role in aligning organizational priorities with customer outcomes. This creates:
- Proactive problem-solving - Identifies risks early, preventing escalations and emergency support tickets
- Customer-centric decision-making - Ensures internal strategies align with real-world customer needs and workflows
- Strategic engagement - Builds long-term relationships that drive retention, growth, and advocacy beyond transactional interactions
💡 Pro Tip: When customers ask "What's the difference between you and Support?", respond: "Support fixes problems when they occur. I work with you proactively to achieve your business goals and prevent problems before they happen. Think of Support as your doctor and me as your health coach."
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
The Trusted Advisor Framework
CSMs succeed when they act as trusted advisors by embodying three core attributes:
Credibility: Deep Product and Industry Knowledge
- Master your product's capabilities, limitations, and roadmap
- Understand your customer's industry trends, challenges, and competitive landscape
- Stay current on best practices and emerging patterns in customer success
- Speak confidently using data and examples to back recommendations
Building credibility:
- Get product certified and continuously test new features
- Read industry publications and analyst reports relevant to your customers
- Study successful customer implementations and document patterns
- Prepare thoroughly for every customer interaction with research and data
Reliability: Consistent Follow-Through and Proactive Communication
- Deliver on commitments without exception - if you say you'll do it, do it
- Provide regular updates proactively, even when there's no new information
- Maintain predictable communication rhythm (weekly, bi-weekly, monthly)
- Be transparent about challenges, delays, and limitations
Building reliability:
- Use task management systems to track every customer commitment
- Set reminders for follow-ups and never miss a promised update
- Under-promise and over-deliver rather than the reverse
- Communicate delays immediately rather than hoping they won't notice
Empathy: Genuine Understanding of Customer Challenges
- Listen actively to understand problems before proposing solutions
- Acknowledge frustrations and validate concerns authentically
- Tailor recommendations to customer's specific context and constraints
- Demonstrate you care about their success, not just your metrics
Building empathy:
- Ask open-ended questions about their business challenges
- Take notes on personal details (team changes, company milestones)
- Reference previous conversations to show you remember and care
- Celebrate their wins as if they were your own
💡 Pro Tip: The Trusted Advisor Framework isn't a one-time achievement - it's maintained through every interaction. One missed commitment can destroy months of built trust. Set a personal standard: "If I say I'll do it, it gets done, period."
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Best Practices for Establishing Your CSM Foundation
- Master the subscription economics → Understand why retention and expansion drive SaaS valuation more than new sales
- Differentiate your role clearly → Know when to act like Sales (consultative), Support (reactive), or neither (strategic partner)
- Build the Trusted Advisor attributes → Develop credibility through expertise, reliability through follow-through, and empathy through listening
- Work across all funnel stages → Don't silo your thinking into "onboarding only" or "renewals only" - think lifetime value
- Balance advocacy and growth → Find win-win solutions where customer success drives company revenue naturally
- Establish feedback loops → Create systematic ways to share customer insights with Product, Marketing, and Sales
- Quantify your role's impact → Use retention metrics, expansion revenue, and NPS to demonstrate CS team value
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
REAL-WORLD APPLICATION
Case Study: Healthcare SaaS Customer Saved Through Trusted Advisor Approach
Initial Situation: At-Risk Enterprise Customer A healthcare SaaS customer ($500k ARR) considered switching to a competitor due to slow implementation progress. They were 6 months into contract with minimal product adoption and growing frustration.
The CSM's Approach: Applying Trusted Advisor Framework
Credibility:
- Researched healthcare compliance requirements affecting their implementation
- Brought in product expert to address technical concerns
- Shared case study from similar healthcare organization's successful rollout
Reliability:
- Conducted weekly calls (instead of monthly) with documented action items
- Sent Friday updates summarizing progress even when minimal
- Met every single deadline promised, no exceptions
Empathy:
- Acknowledged their frustration and validated implementation challenges
- Understood pressure from their CEO to show ROI quickly
- Tailored training to their team's specific workflow and constraints
Results After 4 Months: ✓ Customer achieved full implementation and adoption ✓ Documented 30% efficiency improvement in their workflows ✓ Customer not only renewed but expanded usage by 15% ✓ Became reference customer for other healthcare prospects ✓ CSM received internal recognition for saving at-risk account
Key Strategies Used:
- Applied all three Trusted Advisor attributes systematically
- Over-communicated during crisis period
- Focused on customer outcomes, not just product features
- Balanced advocacy (pushing for realistic timelines) with company goals (preventing churn)
- Documented ROI to justify expansion and renewal
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
KEY TAKEAWAYS: BEST PRACTICES RECAP
✓ CSMs are proactive guides who ensure customers achieve desired outcomes, differentiating from reactive Support and transactional Sales
✓ The role emerged from subscription economics where retention and expansion drive profitability more than new customer acquisition
✓ Three core CSM characteristics: proactive risk/opportunity identification, trust-based relationship building, and balanced advocacy
✓ The CSM Funnel operates across three concurrent stages: Adoption (onboarding), Expansion (growth), and Renewal (retention)
✓ CSMs serve as organizational bridges, feeding customer intelligence to Product, Marketing, and Sales while advocating for customer needs
✓ The Trusted Advisor Framework requires: Credibility (expertise), Reliability (follow-through), and Empathy (genuine understanding)
✓ Retention math proves CS value: 5-point retention improvement on $10M ARR saves $500k annually, far exceeding team costs
✓ Balance customer advocacy with company growth by finding win-win solutions where customer success drives revenue naturally
✓ Establish yourself as translator between customer language and internal business requirements for maximum effectiveness
.png?width=1344&height=768&name=Adobe%20Express%20-%20file%20(1).png)